Windows boot problems are easier to fix when you can identify where the startup process is failing. This guide breaks boot failure into 5 levels, from mild to severe, and explains what each level usually means and what to try next.
How to identify your boot failure level
Restart the PC and note the furthest point you can reach:
-
Do you eventually reach the desktop, but it takes forever? That is Level 1.
-
Do you reach the sign-in screen but cannot log in or the desktop never loads? That is Level 2.
-
Do you get a blue screen, automatic restart loop, or “Automatic Repair” loop? That is Level 3.
-
Do you get a boot message like “Bootmgr is missing” or “No boot device found”? That is Level 4.
-
Do you not even see the Windows logo or manufacturer logo reliably? That is Level 5.
Level 1: Slow boot or hanging boot
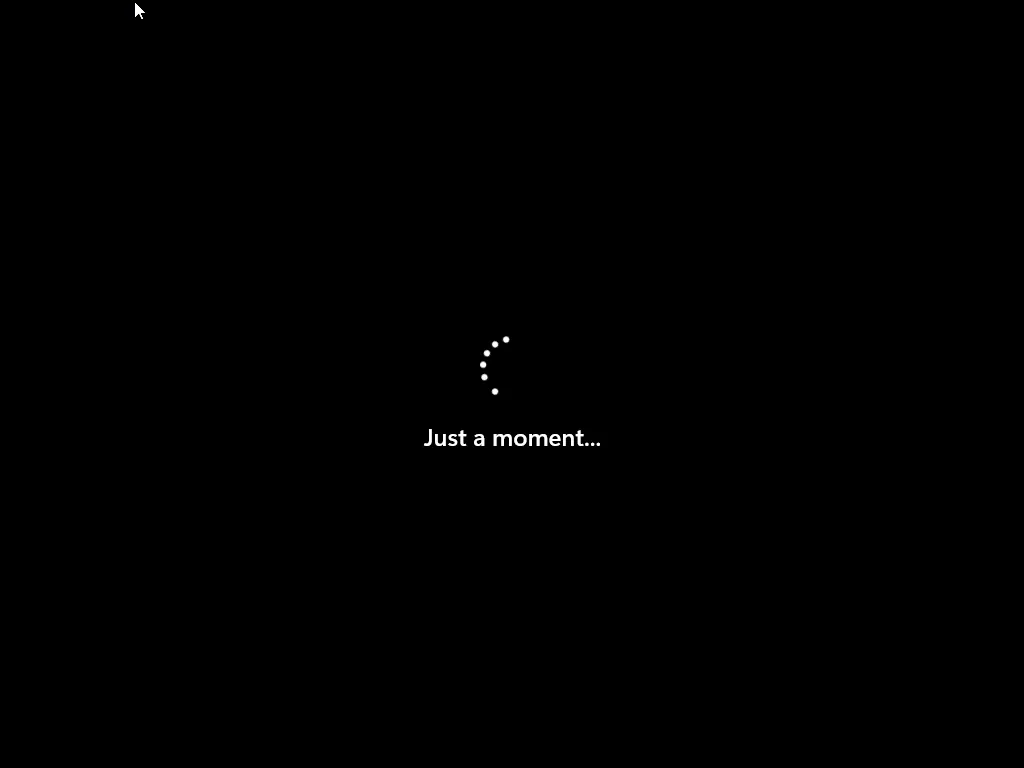
Symptoms
You see a long black screen, spinning dots for a very long time, or the desktop appears but takes a long time to become usable.
Common causes
Too many startup apps, a bad driver, a stuck Windows update, low disk space, or early signs of disk issues.
What to do
-
Disconnect non-essential USB devices and restart.
-
Boot into Safe Mode and disable unnecessary startup apps, then restart normally.
-
If Windows boots normally, run system repairs:
-
sfc /scannow(System File Checker) -
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth(repairs the Windows image)
-
-
Check disk for errors.
Level 2: Login screen failures
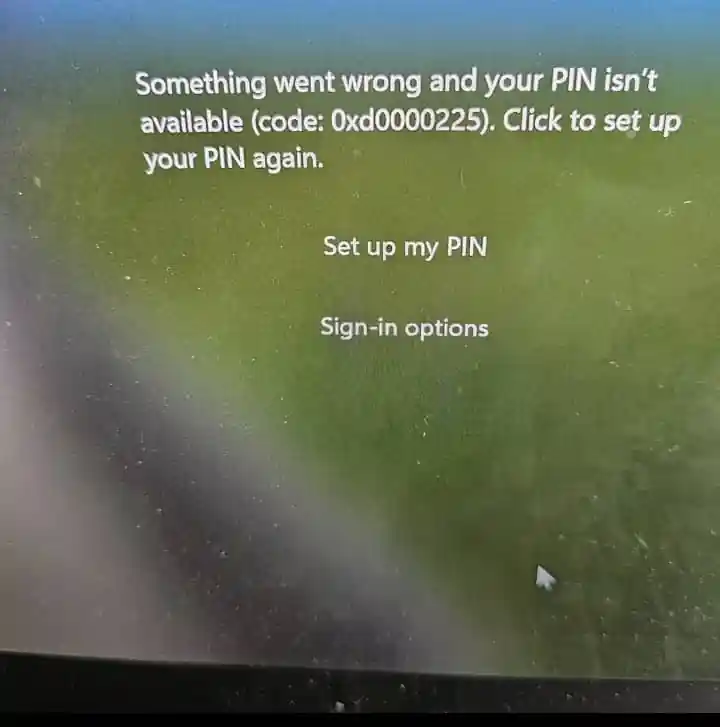
Symptoms
You reach the sign-in screen but cannot sign in, it crashes after sign-in, or you sign in and get a blank screen/desktop never loads.
Common causes
Corrupt user profile, broken Explorer shell, bad startup service, malware, or system file corruption.
What to do
-
If you can open Task Manager with Ctrl + Alt + Delete, run
explorer.exe(File → Run new task). -
Boot into Safe Mode and uninstall any recent security tools, “cleanup tools”, driver utilities, or suspicious apps that were added before the problem started.
-
Run
sfc /scannow, then DISM, then SFC again (same as Level 1). -
If you have multiple user accounts, try signing into a different account. If one account works, the issue may be profile-specific.
-
If you cannot login at all, try system restore from Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE)
Level 3: Windows fails to load (BSOD or infinite restart/repair loop)

Symptoms
Blue Screen of Death (BSOD), automatic restarts, “Preparing Automatic Repair”, or repeated recovery loops before reaching the desktop.
Common causes
Driver conflicts (often graphics/storage), corrupted system files, recent Windows updates, or new hardware.
What to do
-
Enter the Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE) and try Startup Repair.
-
From WinRE, also try:
-
Uninstall Updates (quality update first)
-
System Restore (if restore points exist)
-
-
If you can boot Safe Mode, roll back or update drivers (especially display and storage drivers), then restart.
Level 4: Bootloader errors
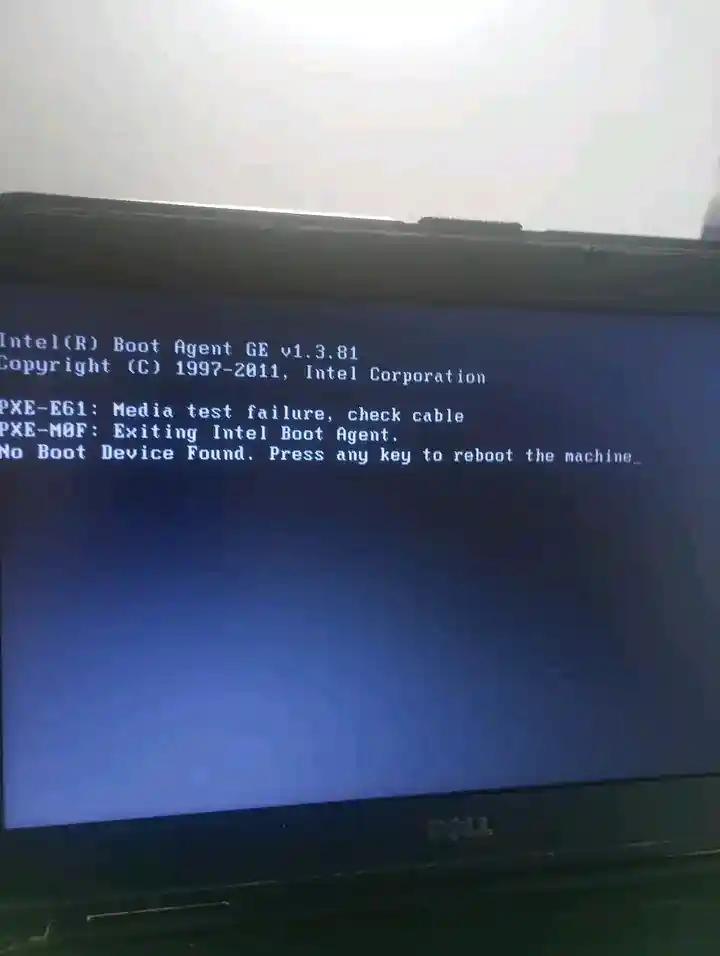
Symptoms
Messages like “Bootmgr is missing”, “No boot device found”, winload.efi errors, or the PC never reaches Windows and shows "Your PC/Device needs to be repaired" on the blue recovery screen.
Common causes
Damaged BCD (Boot Configuration Data), missing boot partition, wrong boot order, UEFI/Legacy mismatch, or a disk that is failing or not being detected.
What to do
-
Enter BIOS/UEFI and confirm the internal drive is detected and Windows Boot Manager (or the internal SSD) is first in boot order.
-
Use WinRE (often via a Windows recovery/installation USB) and try Startup Repair first.
-
If Startup Repair fails, rebuild boot files using BCDBoot from Command Prompt in WinRE.
Level 5: POST failure or no boot

Symptoms
No response, no Windows or manufacturer logo, black screen only, beeping, stuck in BIOS/UEFI, or it powers on but shows nothing.
Common causes
Hardware failure (RAM, SSD/HDD, GPU, motherboard), loose components (after a drop/impact), dead battery, faulty PSU, or corrupted BIOS/UEFI settings/firmware.
What to do
-
Power off, disconnect external devices, and try again with only power + keyboard/mouse.
-
If you are comfortable opening the device, reseat the RAM and storage drive (loose connections are common after impacts).
-
Check BIOS/UEFI: if the SSD/HDD is not detected, treat it as a drive/connection problem until proven otherwise.
-
If there are beeps, look up the manufacturer’s beep code guide for your model (beep patterns are often hardware diagnostics).
At this level, software repair tools (SFC/DISM/Startup Repair) usually will not help until the hardware issue is resolved.
Tools you will hear about at each level
-
Safe Mode (Levels 1–3): helps remove drivers/apps that break startup.
-
SFC/DISM (Levels 1–3): repairs Windows system files.
-
WinRE / Startup Repair / System Restore (Levels 2–4): recovery environment tools.
-
BCDBoot (Level 4): rebuilds Windows boot files.
-
BIOS/UEFI checks (Levels 4–5): confirms the drive is detected and boot mode is correct.
If you want help fast
If you tell me which level you are stuck on (1–5) and what you see on screen (error text or stop code), it becomes much easier to guide the correct recovery path without wasting time on the wrong fixes.
Need more help?
Check the banner below.
