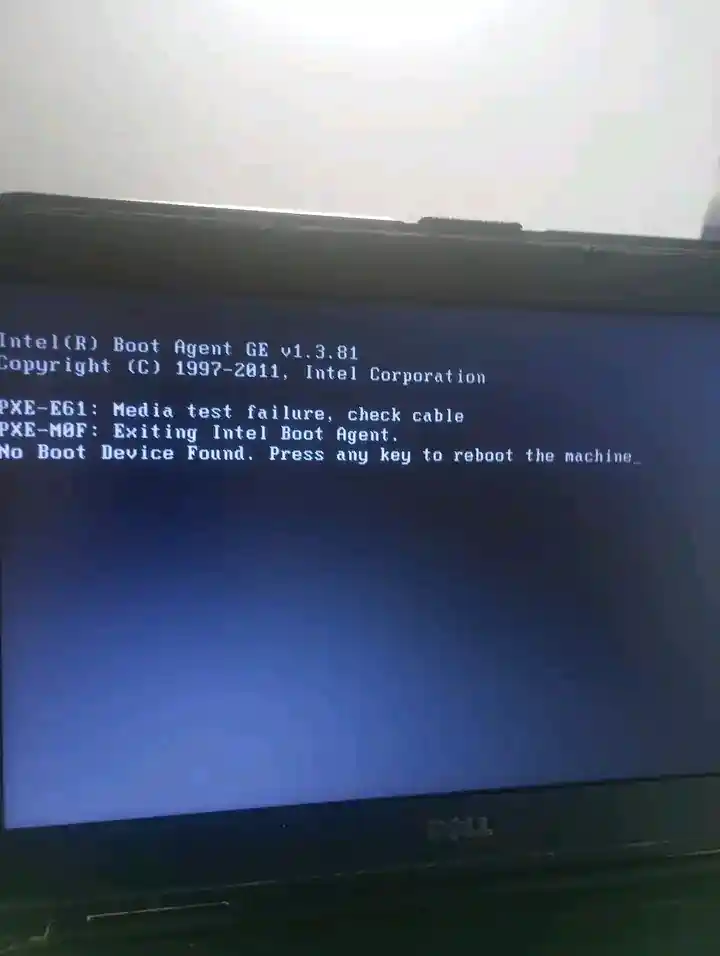
If your PC shows “Boot Device Not Found”, it means your computer cannot find a drive (or boot information) to start Windows. Sometimes it is a simple boot order issue. Other times it is a failing SSD/HDD.
Follow the steps below in order, starting with the easiest checks.
Why does this happen?
“Boot Device Not Found” usually happens because of one of these reasons:
Your PC is trying to boot from the wrong device (for example, USB instead of the internal drive).
The SSD/HDD is not detected properly (loose connection, failed drive, or BIOS/UEFI can’t see it).
The boot files are damaged (Windows Boot Manager/BCD issue), often after an update, power loss, or cloning to a new drive.
UEFI/Legacy boot settings changed, so the system is looking for boot files in the wrong format.
Before You Start
-
Turn the PC off completely.
-
Unplug all USB devices (flash drives, external drives, memory cards, printers).
-
Turn it back on and check if the error is gone.
This fixes cases where the PC is accidentally trying to boot from a non-bootable USB. If that didn't help, try the steps below.
How to Fix:
1) Check if your SSD/HDD is detected in BIOS/UEFI
-
Turn on the PC and immediately press the BIOS/UEFI key repeatedly (common keys are F2, Del, Esc, or F10, depending on the manufacturer).
-
In BIOS/UEFI, look for Storage, Boot, or System Information.
-
Confirm whether your internal SSD/HDD is listed.
-
Run the disk diagnostic tool provided by the PC manufacturer
If the drive is not listed, skip to 4. This strongly points to a hardware/connection problem.
2) Fix the boot order and select Windows Boot Manager
If the drive is detected, the next common problem is boot order.
-
In BIOS/UEFI, go to the Boot section.
-
Set Windows Boot Manager (or your internal SSD/HDD where Windows is installed) as the first boot option.
-
Save changes and exit (usually F10).
If you see both “UEFI: drive name” and “Legacy: drive name,” prefer the UEFI option on modern systems or BIOS if your device is older.
3) Check UEFI vs Legacy boot mode
A mismatch here can cause “boot device not found” even when the drive is fine.
-
In BIOS/UEFI, look for Boot Mode, UEFI/Legacy, or CSM settings.
-
If Windows was installed in UEFI mode (common on Windows 10/11 systems), set boot mode to UEFI. Try switching modes or using Hybrid if you're unsure.
-
Save and restart.
If you recently cloned a drive or changed BIOS settings, this step is especially important.
4) Reseat the physical drive
This helps when the drive was not firmly installed, or the laptop/PC suffered an impact (drop, knock, rough movement).
-
Turn the PC off and unplug power.
-
If it is a laptop and the battery is removable, remove it. Hold the power button for 10 seconds.
-
Open the back cover (only if you are comfortable doing so).
-
Reseat the drive:
-
For M.2/NVMe SSD: unscrew it gently, remove it, then insert it firmly and screw it back.
-
For 2.5" SATA SSD/HDD: check the connector/cable is properly seated.
-
-
Reassemble and boot again.
If you are not comfortable opening the device (or it is under warranty), it is safer to use a technician.
5) Drive is detected but still won’t boot: use Windows recovery tools
If BIOS/UEFI detects the drive but Windows still cannot boot, you will usually need a Windows recovery/installation USB to access repair tools (WinRE).
-
Boot the PC from the Windows USB.
-
On the Windows Setup screen, select Repair your computer (do not choose Install yet).
-
Go to Troubleshoot → Advanced options and try these in order:
Start with Startup Repair
This attempts to fix common boot issues automatically.
Run a disk check
Open Command Prompt and run:
chkdsk C: /f
In recovery, Windows may not be on C:. If needed, identify the correct drive letter first, then run CHKDSK on that letter.
Rebuild Windows boot files
In Command Prompt, use BCDBoot to recreate boot files:
bcdboot C:\Windows
If needed on UEFI systems:
bcdboot C:\Windows /s S: /f UEFI
6) If the drive is dead: you have to replace it
If the SSD/HDD is not detected in BIOS/UEFI, disappears randomly, freezes the PC, or makes unusual noises (HDD), treat it as drive failure.
At that point the fix is usually:
-
Buy a new SSD/HDD.
-
Install Windows on the new drive.
-
Restore your files from backup (or attempt professional data recovery if the files are critical).
Extra note: prevent this situation next time
A lot of “Boot Device Not Found” stories end badly because there was no backup.
To reduce risk:
-
Run disk checks when you notice errors or unusual slowdowns (not constantly).
-
Use Optimize Drives (Windows’ built-in tool). It defragments HDDs and sends TRIM commands for SSDs.
-
Most importantly: backup! backup!! backup!!
Disaster recovery becomes a simple restore when your data is already safe.