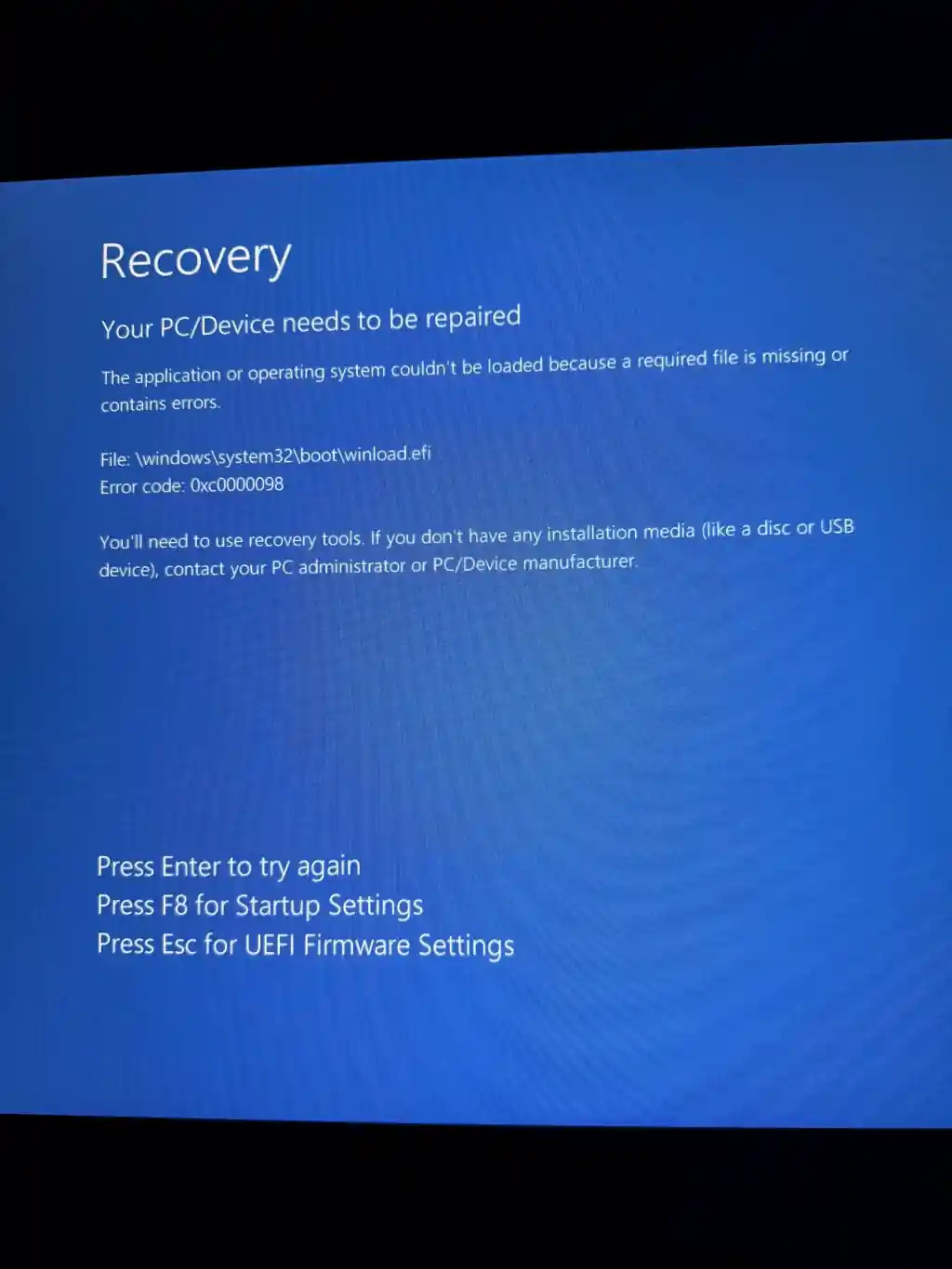
This guide applies to the Windows Recovery screen that says:
-
Your PC/Device needs to be repaired
-
File:
\windows\system32\boot\winload.efi -
Error code:
0xc0000098
This usually means Windows cannot load because the boot configuration data (BCD) or related boot files are missing or corrupted. This is a very common boot issue with Windows and can be easily fixed.
Why this error occurs?
Windows is installed on your drive, but your PC cannot find the correct boot information to start it. This commonly happens after an interrupted update, sudden power loss, disk errors, or a failed clone/migration to a new drive. It can also happen if BIOS/UEFI settings changed or the PC is trying to boot the wrong device. When critical files needed to boot up Windows becomes corrupted or missing, Windows fails to boot and this screen appears.
Quick Fixes
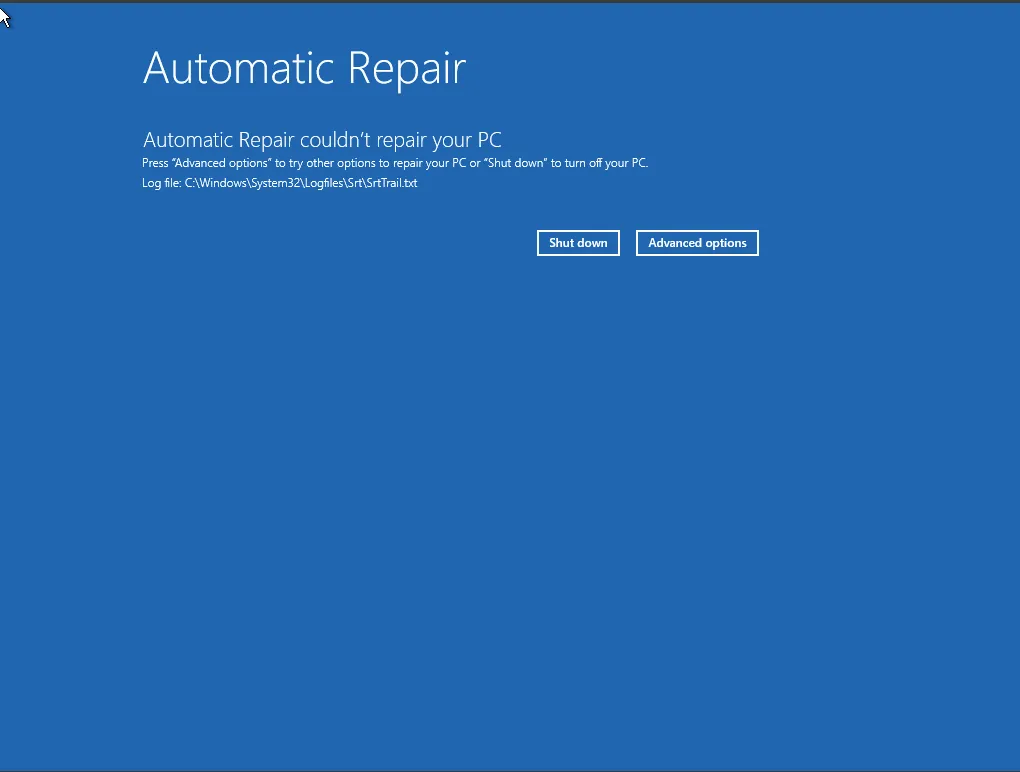
Windows usually attempt to fix boot errors automatically but if you're not lucky and Automatic Repair doesn't seems to fix the issue, here are quick fixes you can try:
1) Try Startup Repair from Windows Recovery Tools
You will need Windows Recovery tools. If your PC does not show a “Troubleshoot” menu by itself, you may need a Windows installation USB. See how to get one here
-
Boot into Windows Recovery (WinRE) or boot from a Windows USB.
-
Select Repair your computer.
-
Go to Troubleshoot → Advanced options → Startup Repair.
-
Select your Windows installation/account if prompted.

If Startup Repair fixes the issue, your PC should boot normally.
2) Rebuild boot files using Command Prompt
Use this if Startup Repair does not work.
-
Boot into Repair your computer again.
-
Go to Troubleshoot → Advanced options → Command Prompt.
Now run these steps carefully.
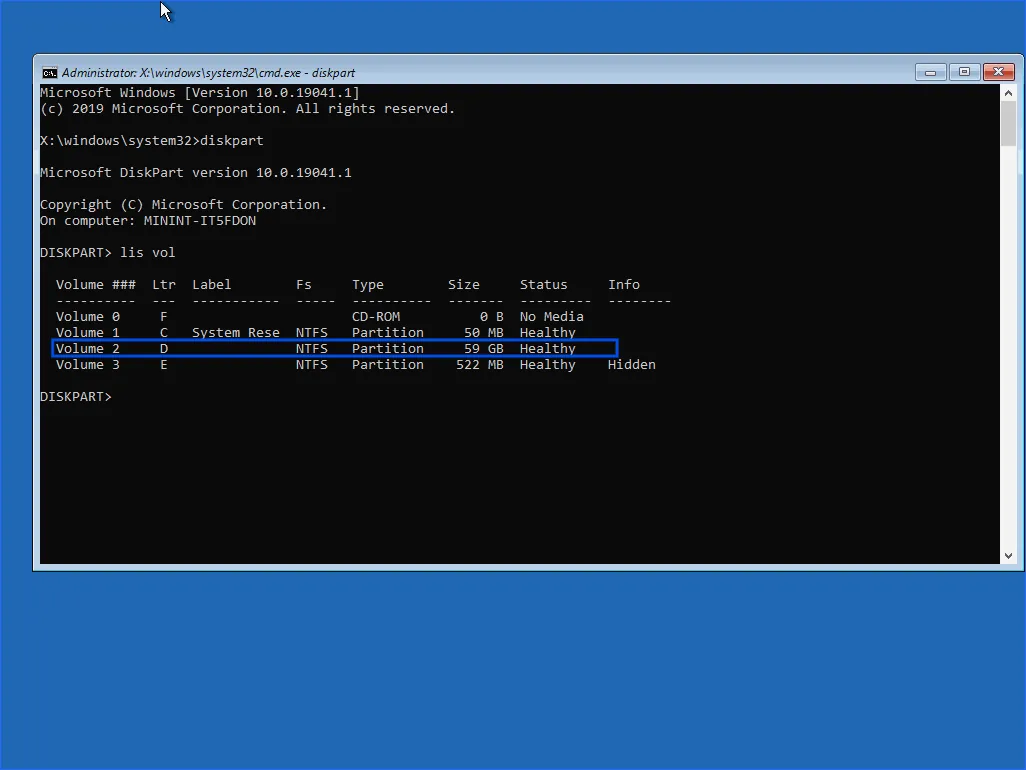
Step A: Find the Windows drive letter in Recovery
Drive letters can change in Recovery, so Windows might not be C: here.
Type: diskpart
Then: list vol
Look for the volume that contains Windows (often the largest NTFS partition). Note its letter (example: D).
Type:
Step B: Check the disk for errors
Replace D: with your Windows drive letter:

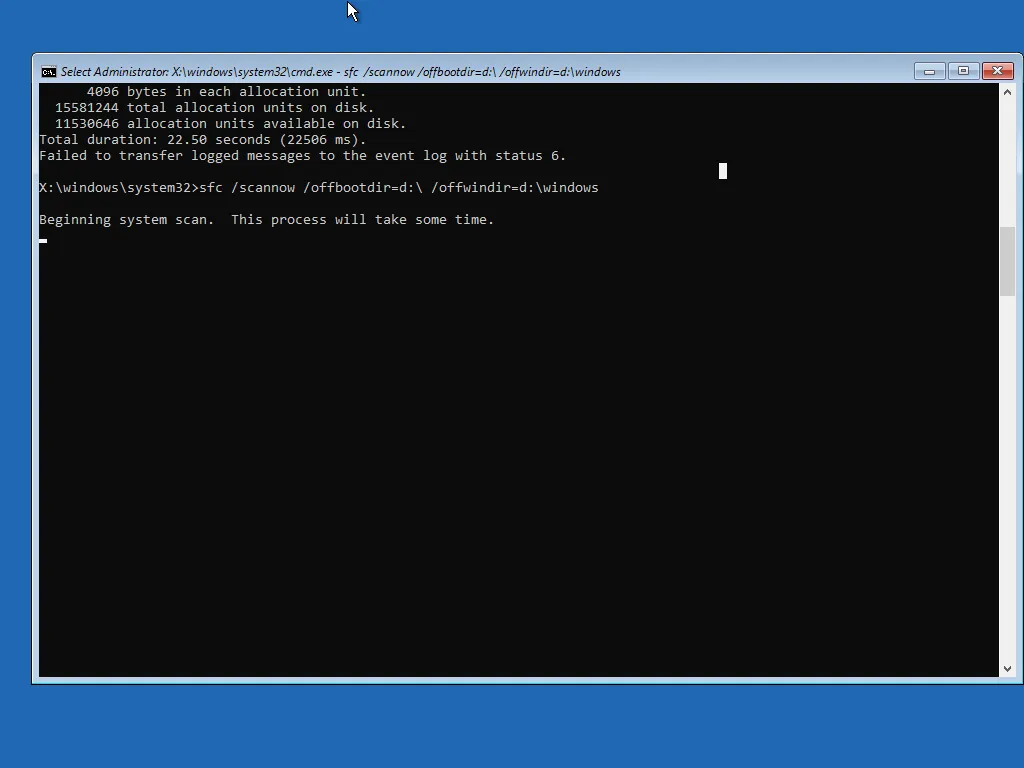
Step C: Repair Windows system files (offline)
Replace D: if needed:
Step D: Recreate boot files (often fixes winload.efi/BCD issues)
This step writes fresh boot files for your Windows install.
Replace D:\Windows if your Windows folder is on a different letter:
bcdboot D:\Windows
If your PC is UEFI-based (most modern systems), you may need to specify the UEFI boot mode. If the simple command above fails, use:
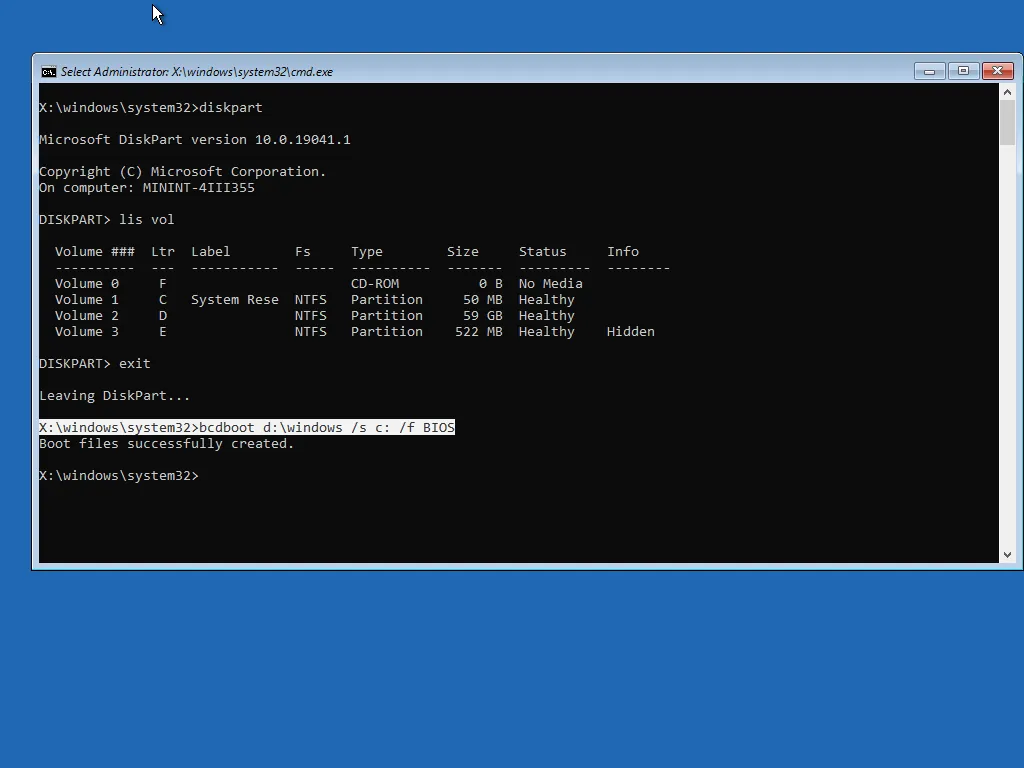
- Close Command Prompt and restart the PC.
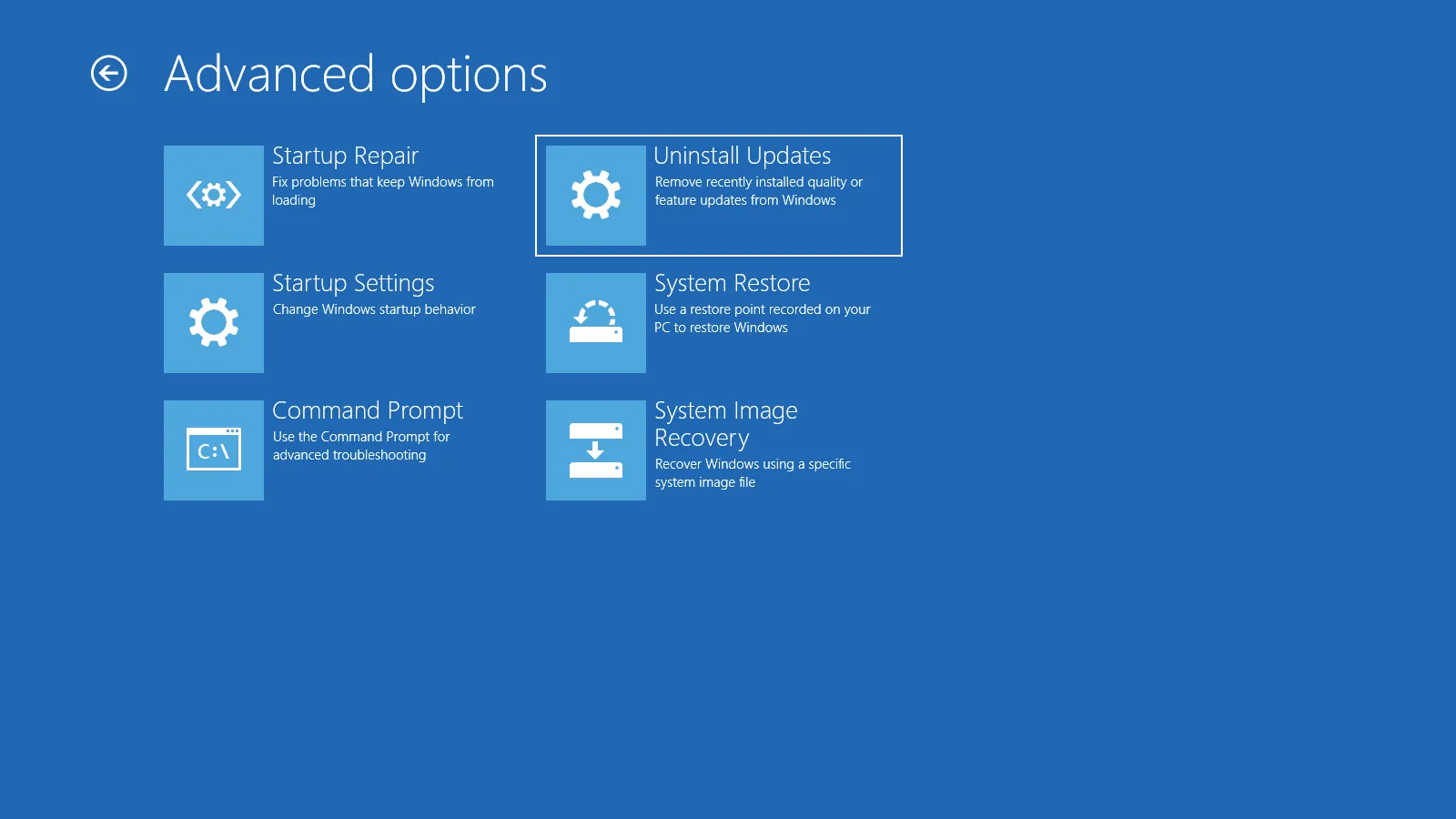
3) Uninstall the latest update
If this started right after an update, rolling it back can help.
-
Go to Troubleshoot → Advanced options → Uninstall Updates.
-
Try Uninstall latest quality update first.
-
If needed, try Uninstall latest feature update.
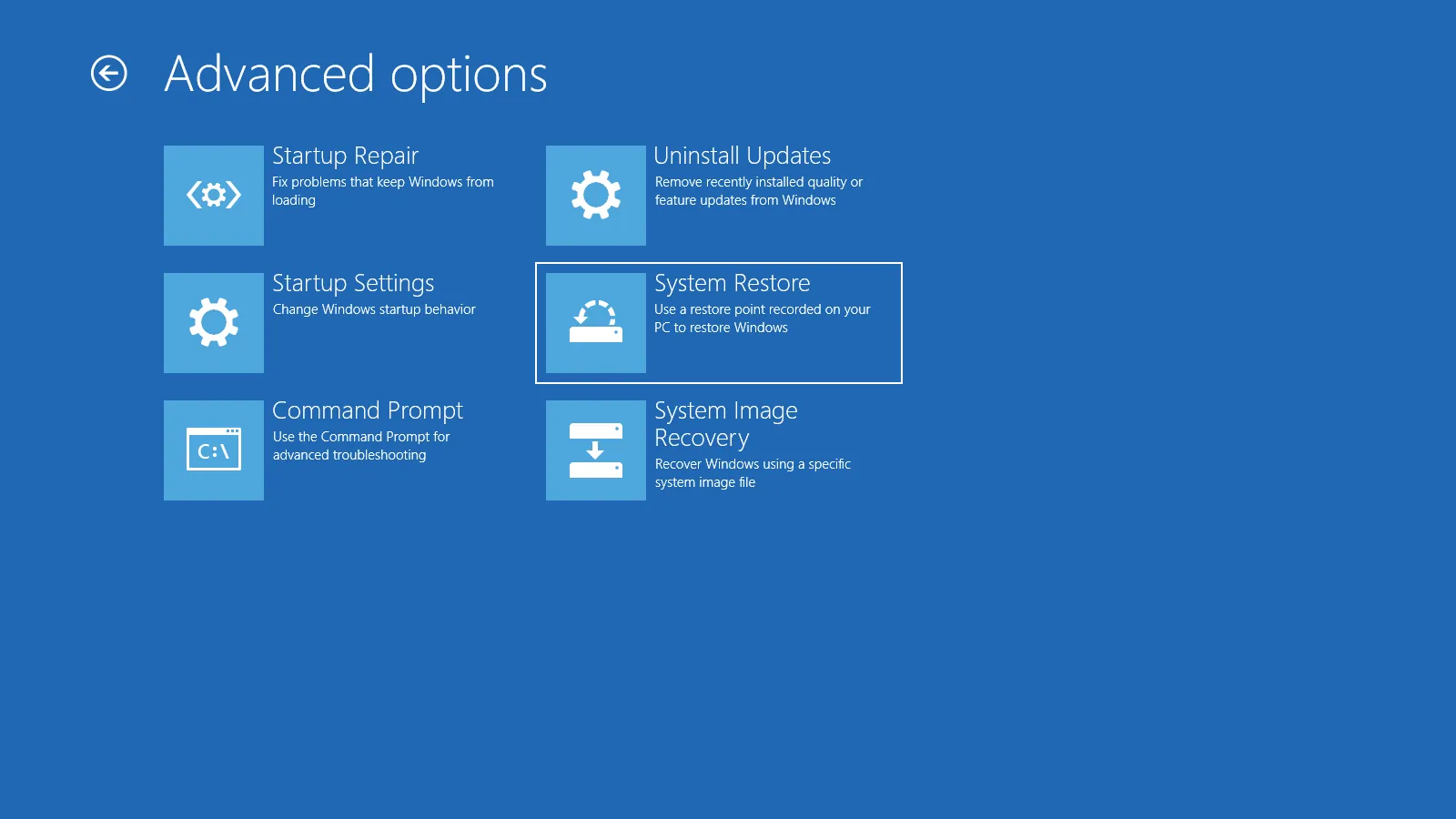
4) System Restore
If System Restore was enabled, this can roll your system back to a working point.
-
Go to Troubleshoot → Advanced options → System Restore.
-
Select a restore point dated before the problem started
When to Escalate
Stop repeated repair attempts and switch to hardware checks (and data-first thinking) if any of the following is true:
-
The internal SSD/HDD is not detected in Windows Recovery tools or in BIOS/UEFI.
-
CHKDSK reports many bad sectors, or it keeps failing mid-scan.
-
The PC keeps returning to the same Recovery screen (winload.efi / 0xc0000098) even after Startup Repair and rebuilding boot files with BCDBOOT.
In these cases, the issue is often a failing drive or deeper corruption. The priority should be backing up your important files before the drive becomes unreadable.
If things don’t go as planned
If you’ve tried the steps in this guide and your PC still won’t boot, contact a Windows technician so we can fix it without making the situation worse.
Message me with:
-
A clear photo of the error screen (showing winload.efi and 0xc0000098)
-
Your PC brand/model
-
Whether you were doing an update, shutdown, clone, or install before this started
-
Whether BitLocker/device encryption is enabled (if you know)
You can request for support here.