How to Recover Deleted Files on Your Windows PC
This guide helps you recover files you deleted on Windows 11 or Windows 10, whether they were deleted normally, deleted from the Recycle Bin, or removed with Shift+Delete.
What This Usually Means
When you delete a file, Windows often removes it from view first (Recycle Bin). If it is permanently deleted, the data may still be recoverable until Windows overwrites that space. The faster you act, the better your chances.
Before You Start
-
Stop using the drive where the file was deleted. Do not install apps, download files, or copy large folders. This reduces the chance of Windows overwriting the deleted data.
-
If the deleted file was on your Desktop/Documents/Pictures and you use OneDrive, check OneDrive first (it is often the easiest win).
-
If the file was deleted from an SSD, recovery can be harder because SSDs may permanently clear deleted blocks using TRIM.
How to Fix It
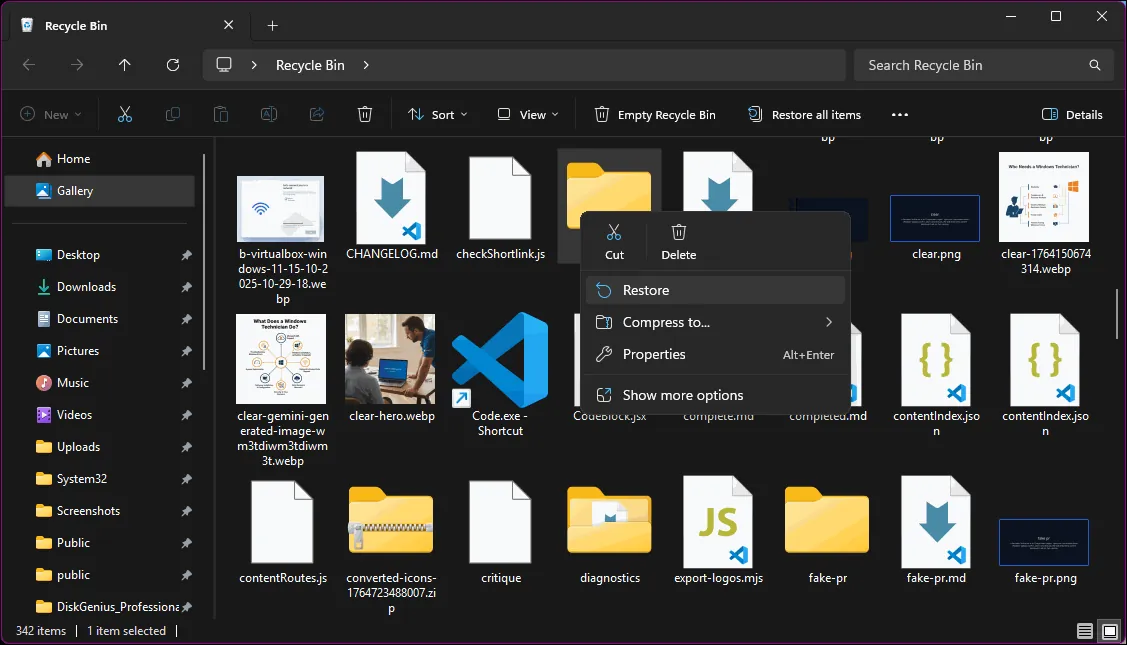
1) Check the Recycle Bin first
-
Open Recycle Bin on your Desktop.
-
Use the search box (top-right) to search the file name.
-
Right-click the file and select Restore.
The file will return to its original location.
2) Check OneDrive (if your files were syncing)
If your PC was backing up folders to OneDrive, the file may still be in OneDrive’s recycle bin.
-
Go to the official website
-
Sign in with the Microsoft account you use on that PC.
-
Open Recycle bin.
-
Select the file and choose Restore.
3) Restore from File History (if it was enabled)
File History automatically keeps copies of your personal files when set up.
-
Open Control Panel.
-
Go to System and Security → File History.
-
Select Restore personal files.
-
Browse to the folder where the file was, choose a version/date, then click Restore.
4) Use Disk Drill (easy file recovery tool)
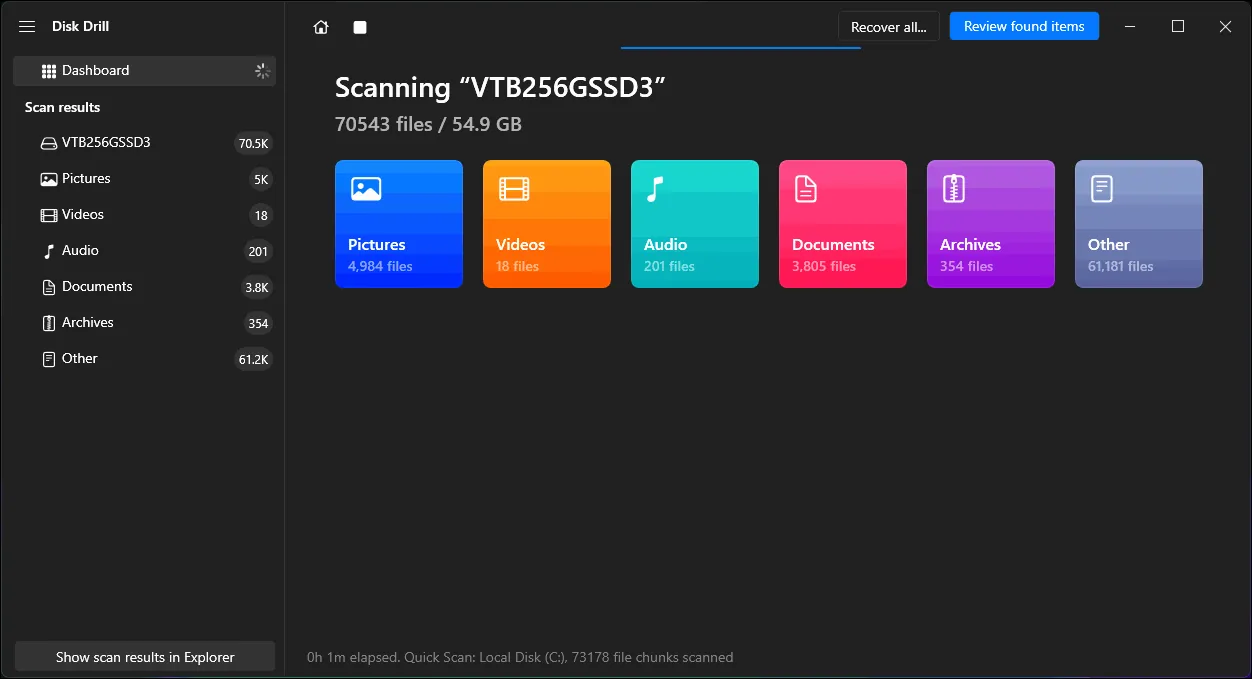
Disk Drill is useful when the file is not in Recycle Bin and you do not have backups. It scans the drive for recoverable deleted files.
Important safety rules:
-
Install Disk Drill on a different drive than the one you are recovering from (if you can).
-
Recover files to a different drive (external drive recommended).
Basic steps:
-
Download and install Disk Drill for Windows.
-
Open Disk Drill and select the drive where the file was deleted.
-
Start a scan and wait for results.
-
Preview files (if available), select what you need, then recover them to another drive.
Disk Drill (CleverFiles) official site
5) Use DiskGenius (good for deeper scans and partition-related issues)
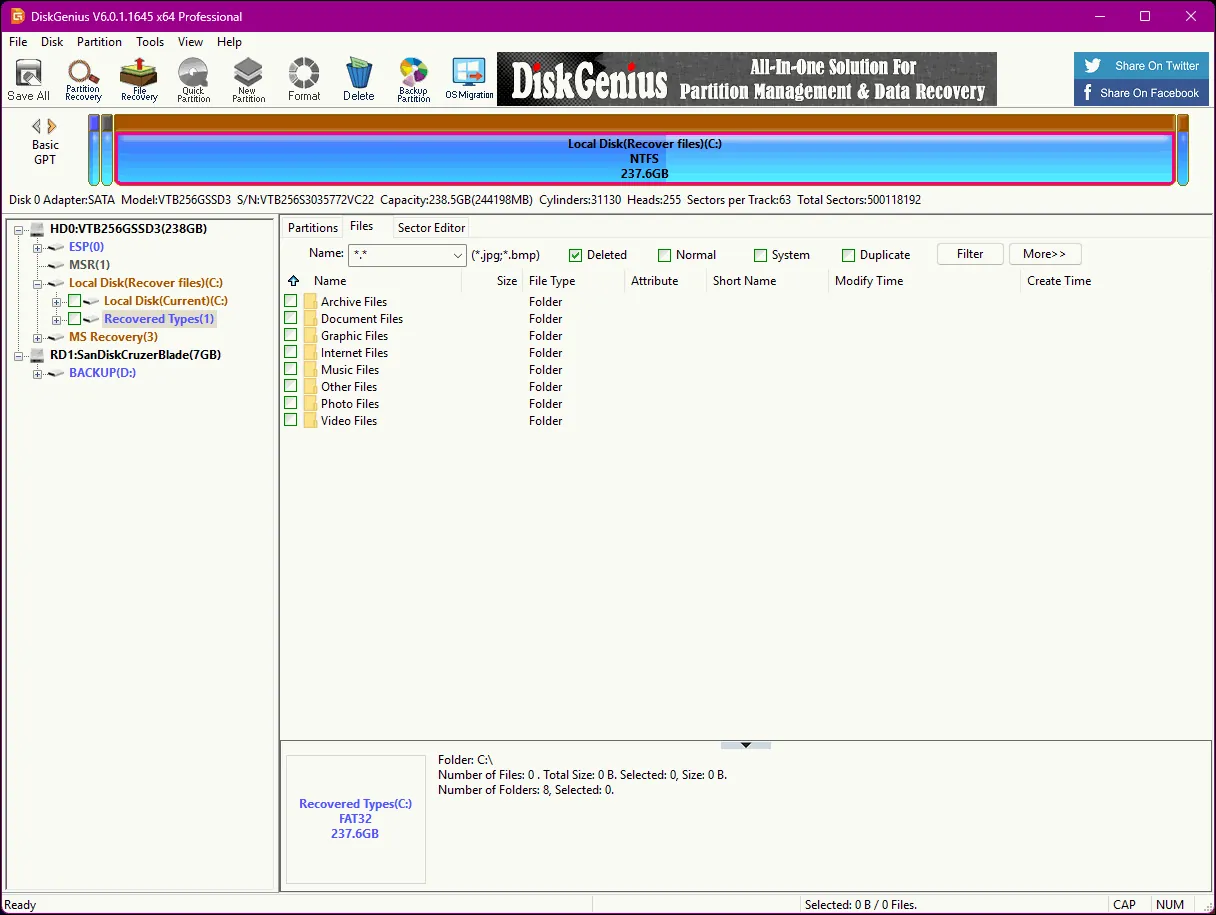
DiskGenius can help with deleted file recovery and is also commonly used when the problem involves partitions, formatting, or a drive that looks “empty” after an issue.
Important safety rules:
-
Do not install DiskGenius on the same drive you are recovering from if you can avoid it.
-
Always recover to a different drive.
Basic steps:
-
Download and install DiskGenius.
-
Open it and select the affected disk/partition.
-
Use its recovery feature (commonly labeled as recovering lost/deleted files).
-
Scan, preview, then recover the files to an external drive or another internal drive.
DiskGenius official site
6) Use professional data recovery services (recommended for hardware failure)
If you suspect hardware problems, software recovery attempts can make things worse. Consider professional recovery services if:
-
The drive is not detected in BIOS/UEFI or Disk Management.
-
The PC makes unusual sounds (clicking/grinding from an HDD).
-
The drive disconnects randomly, shows 0GB, or causes frequent freezing.
-
You smell burning, the laptop had liquid damage, or it suffered a heavy drop.
In those cases, the priority is protecting what is left on the drive, not repeated scanning.
7) Set up backups now (so next time recovery is easy)
File recovery is stressful because you are trying to “undo” a disaster after it has already happened. A proper backup turns the same situation into a simple restore: no scanning tools, no guessing, and no panic. Once you recover what you can, take a few minutes to put a backup system in place so the next deleted file is a two-click fix.
If That Doesn’t Work
-
If it is a work laptop, your organization may have backups (Microsoft 365, endpoint backup, or server profiles). Contact your IT team.
-
If the drive is making unusual noises (HDD clicking) or disappears sometimes, stop attempting recovery. This can be a failing drive.
-
If the file is extremely important, consider a professional data recovery service. The wrong steps can reduce the chance of recovery.
When to Contact a Windows Technician
Contact a technician (or me, if you want me to handle it) if:
-
The file was deleted from an SSD and you cannot find it in backups
-
Recycle Bin/OneDrive/File History do not have it
-
You need to use a Data Recovery Software but do not want to risk doing it incorrectly
-
The PC is unstable or the drive looks like it is failing
